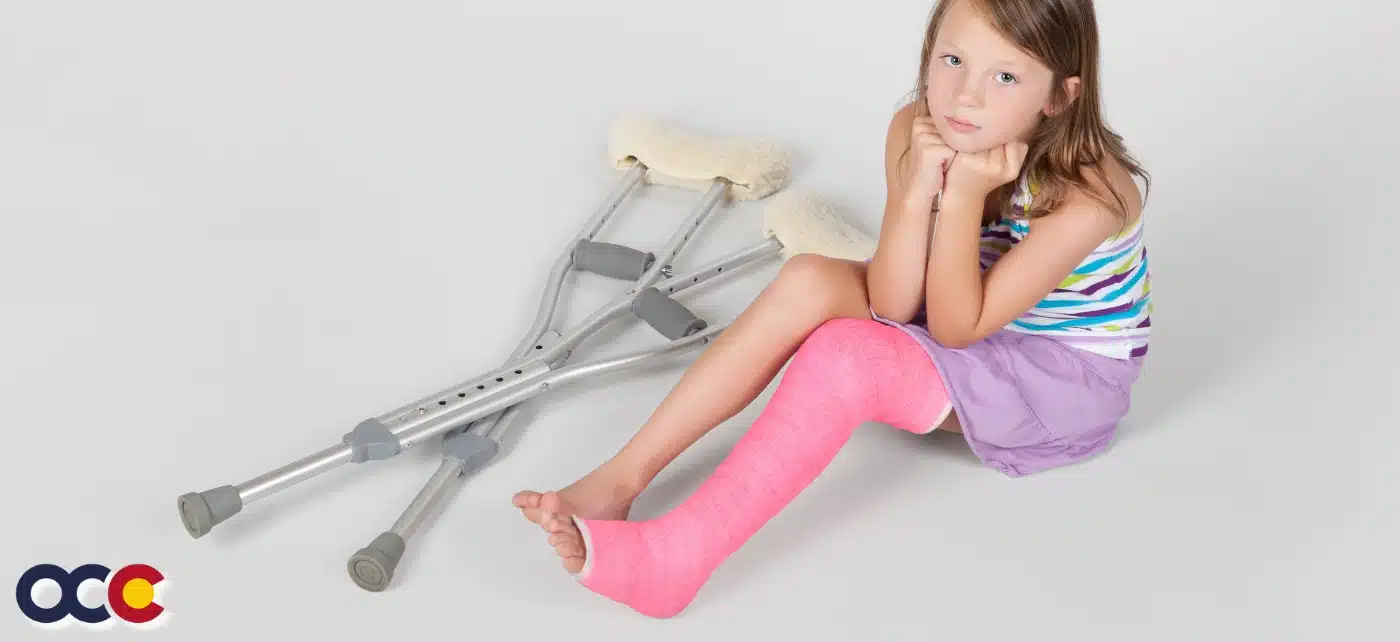
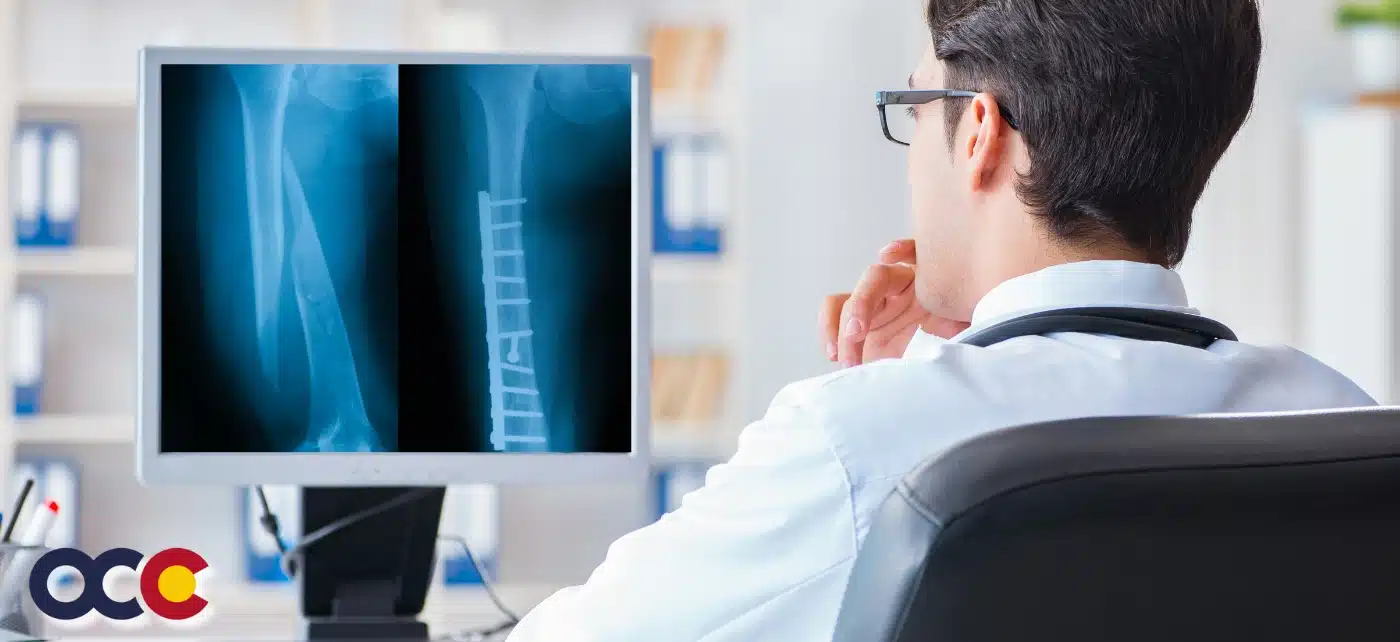
Most people don’t know what their tibia is or even where it is located. What is important to know is that the tibia is a weight-bearing bone and plays a crucial role in supporting the body’s weight during activities like standing and walking. Tibia shaft fractures are not only painful, but they may prevent you from moving your leg or putting any weight on it. This can have a serious impact on your life, and that is why you should see a specialized orthopedic surgeon as soon as possible at OCC – Advanced Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Specialists in Denver, Parker, or Aurora, Colorado. Untreated tibia shaft fractures can have serious consequences.
OVERVIEW
The lower leg has two bones in it: the tibia and the fibula. The tibia is the major bone that serves as the primary support of the leg. The shaft is the middle of that bone, which is why it is commonly referred to as the shin bone. It is the most often fractured long bone in the body. Males have the highest incidence of tibia shaft fractures and present with the highest frequency between the ages of 10 and 20, whereas women have the highest frequency between the ages of 30 and 40. Tibia shaft fractures are a common pediatric fracture. Young children and toddlers are at risk for tibial shaft fractures, even when the force of injury is low. Pediatric tibia shaft fractures are the third most common long bone fracture in children, accounting for 10 to 15 percent of all pediatric fractures. Tibia shaft fractures in children under six, are often called “toddler’s fracture”. They are most common in children in the early years of walking – 9 months to 3 years. A toddler’s fracture is a spiral fracture of the tibia without any injury to the fibula.
ABOUT THE TIBIA
The tibia is one of the two long bones in the lower leg, with the other being the fibula. The shaft of the tibia refers to the long, cylindrical portion of the bone between the proximal (near the knee) and distal (near the ankle) ends. It is also known as the diaphysis. It is closer to the inside of the body (medial) than the fibula or smaller lower leg bone. The tibia is the second longest bone in the body and the most commonly fractured long bone in the body. It is a vital part of the knee and ankle joints. It must heal straight to allow these joints to work well. Many important muscles also attach to this bone, which helps the thigh, leg, and foot muscles work properly. The shaft of the tibia includes the anterior border, posterior surface, soleal line, and lateral border.
WHAT IS A TIBIA SHAFT FRACTURE?
Tibia shaft fractures vary greatly, depending on the force that causes the break. Tibia shaft fractures can be:
- Nondisplaced: a fracture where the broken bones remain aligned. This type of fracture is usually seen in children under four.
- Displaced, noncomminuted: a fracture where the bones are broken in no more than two pieces (noncomminuted) but are not aligned. This is an isolated fracture of the tibia shaft with an intact fibula. It is the most common tibia shaft fracture.
- Displaced, comminuted: a fracture where the bones are broken in several fragments and not aligned.
Many doctors describe tibia shaft fractures using classification systems depending on the following:
- The location of the fracture (the tibial shaft is divided into thirds: distal, middle, and proximal)
- The pattern of the fracture (for example, the bone can break in different directions, such as crosswise, lengthwise, or in the middle)
- If the skin around the fracture is intact (closed fracture)
- Whether a bone breaks in such a way that bone fragments stick out through the skin or a wound penetrates down to the broken bone. This type of fracture is called an open or compound fracture. Open fractures often involve much more damage to the surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments. They have a higher risk for complications—especially infections—and take a longer time to heal.
Read more about Tibia Shaft Fractures on our new Orthopedic News Site – Colorado Orthopedic News. Schedule an appointment with a leg or Sports Medicine specialist today.